The most comprehensive chapter on ceramic chip capacitors (MLCCs) ever written, a must-have for every electronics engineer.
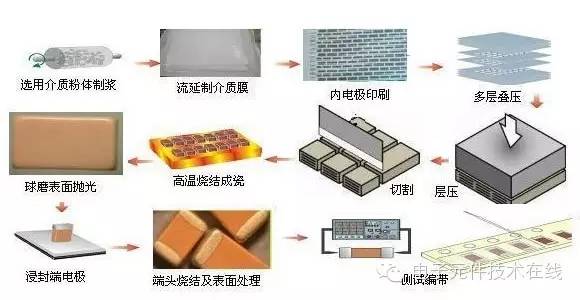
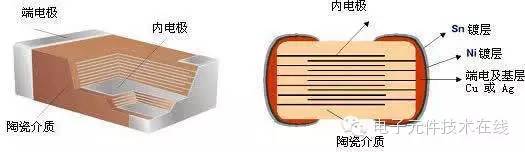
Multilayer Chip Ceramic Capacitor — commonly referred to as a chip capacitor or chip capacitor. In Japan and Taiwan, it is often called a multilayer capacitor or laminated capacitor. MLCC stands for Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitor. Invented by Americans in the 1960s, it was further developed and mass-produced in Japan during the 1980s using low-cost base metals.
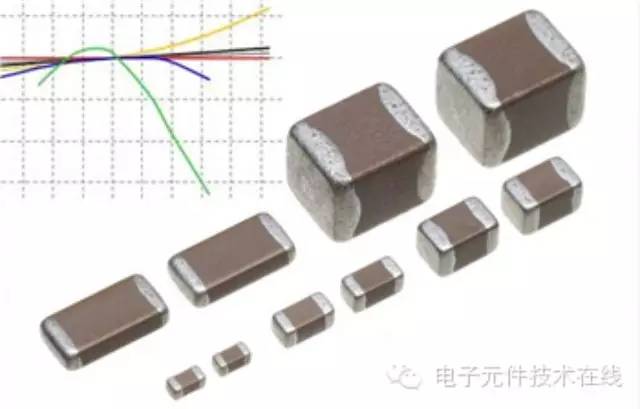
Size series are standardized and commonly represented in inches: 0603 means length 0.06 inch (1.6 mm), width 0.03 inch (0.8 mm). In the International System of Units, 1608 indicates length 1.6 mm and width 0.8 mm.
| Table 1: SMD Capacitor Full Series Size Chart |
| 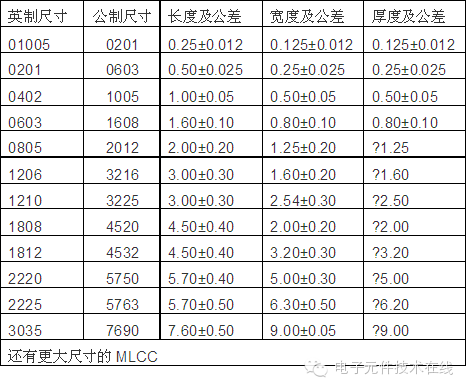 |
The smallest size available is 01005 (0.25 mm × 0.125 mm), currently produced in limited quantities by only a few Japanese companies. Sizes like 0201, 0402, and 0603 are widely used and can be mass-produced by major manufacturers. Shenzhen Yuyang specializes in small-sized MLCCs. Larger sizes like 2220 and above are less common, mainly produced by smaller and mid-sized companies.
**Rated Voltage Series:**
- Low voltage: 3.3V, 6.3V, 10V, 16V, 25V, 50V
- Medium voltage: 100V, 200V, 250V, 500V, 630V
- High voltage: 1000V, 2000V, 3000V
- Ultra-high voltage: 4000V, 5000V, 8000V
Low-voltage MLCCs (3.3V–16V) are often used to replace electrolytic capacitors due to their high capacitance. The most common products fall in the 25V–50V range. Medium-voltage capacitors (100V–630V) typically come in 0805 and larger sizes. High-voltage ones (1000V–3000V) are usually 1206 and up, while ultra-high-voltage (4000V+) are found in 2220 and larger sizes. Japanese brands dominate the low-voltage and high-capacity market, while TDK, Fenghua Hi-Tech, and Heshentang lead in medium and high-voltage applications.
**Material (Ceramic Dielectric):**
MLCCs use two main types of dielectric materials: paraelectric (Class I) and ferroelectric (Class II). Class I materials have stable temperature characteristics, while Class II offer higher capacitance but with more variation. EIA has established standards for both types.
| Table 2: Class I Dielectric Temperature Coefficient |
| 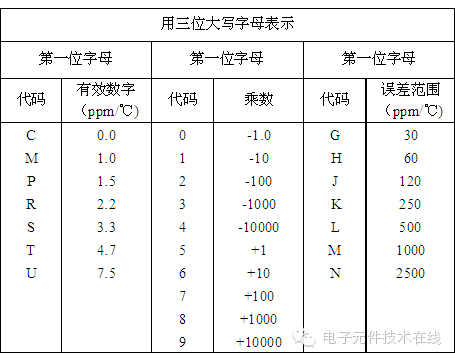 |
For example, COG (or NPO) has a temperature coefficient of ±30 ppm/°C, suitable for high-frequency and precision circuits.
| Table 3: Class II Dielectric Temperature Characteristics |
| 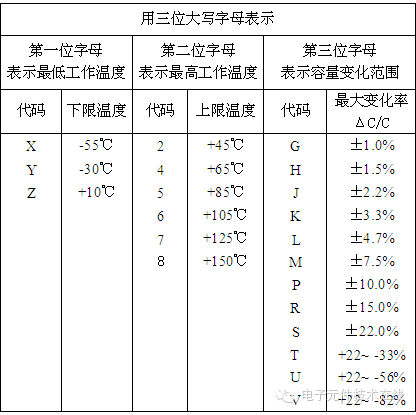 |
X7R, for instance, operates from -55°C to 125°C with ±15% capacitance variation.
**Common Materials Used in MLCCs:**
1. **NPO (COG)**: Doped strontium zirconate (SrZrO3), offering excellent stability. It is ideal for high-frequency applications such as oscillators and RF circuits.
2. **X7R/X5R**: Doped barium titanate (BaTiO3), providing higher capacitance but with less stability. Widely used in non-high-frequency circuits.
3. **Z5U/Y5V**: Doped barium strontium titanate (BaSrTiO3), offering even higher capacitance at lower cost but with poor stability and reliability.
Due to advancements in X7R/X5R technology, their capacitance levels are now close to those of Z5U/Y5V, but Z5U/Y5V still suffer from high losses and poor reliability, leading to their gradual decline.
**Capacitance and Tolerance Levels:**
- **NPO (COG)**: Typically ±5% tolerance, suitable for smaller values.
- **X7R**: ±10% tolerance, with a wide range from 100 pF to 47 µF.
**Naming Rules:**
A typical MLCC part number includes: size, temperature characteristics, capacitance value, tolerance, voltage rating, electrode material, and packaging. For example:
**0805X7R104K500NT**
- 0805: Size (0.08" x 0.05")
- X7R: Temperature characteristic
- 104: Capacitance (100,000 pF = 100 nF)
- K: Tolerance (±10%)
- 500: Rated voltage (50 V)
- N: Electrode material (nickel)
- T: Packaging type (tape)
**Major Brands and Naming Conventions:**
Leading manufacturers include Murata, TDK, Kyocera, Taiyo Yuden (Japan), Samsung (South Korea), and Fenghua Hi-Tech, Yuyang (China). Each brand has its own naming convention, but they all follow similar parameters.
**Purchasing Considerations:**
When selecting an MLCC, consider: size, required accuracy, voltage rating, capacitance value, loss factor, dielectric strength, and DC bias characteristics.
**Price Factors:**
The price depends on production volume. Standardized, mass-produced MLCCs are generally cheaper, while custom or specialized parts may cost more.
Wireless Router
The name of wireless router can be separated out of two keywords: wireless and routing. Understand the technical principle behind these two words, you understand the wireless router.
Wireless is also what we often call Wi-Fi. Wireless routers can convert home broadband from wired to wireless signals, and all devices can happily surf the Internet as long as they connect to their own Wi-Fi. In addition, these devices also form a wireless local area network, where local data is exchanged at high speed and is not limited by the bandwidth of home broadband.
For example, many people have smart speakers in their homes that can be used to control various smart appliances. When you say small X small X, turn on the TV, the speaker actually finds the TV through the LAN and sends instructions, and does not need to connect to the Internet; And if you let it broadcast news, you have to get data through the Internet.
The Local Area Network we talked about earlier, also known as the Intranet, is represented by the Local Area Network (LAN) on the router, so the Wi-Fi signal is also called WLAN(Wireless LAN); The Internet we want to access, also known as the extranet, is represented on the router by the WAN(Wide Area Network).
On the Intranet, the IP address of each device is different, which is called a private address. All devices on the Internet share the same public address, which is assigned by broadband operators such as China Telecom Unicom.
The router is the bridge between the Intranet and the external network. The above mentioned IP address translation, packet forwarding, is the router routing function.
In other words, the router is the hub of the home network, and the data of all the devices must be forwarded through it to access each other or reach the external network, which means that one husband is the key and ten thousand men are not open, so the comprehensive router is also called "home gateway".
Wireless Router,Wifi 6 Wireless Router,Mesh Wifi Router,Wifi Routers For Home
Shenzhen MovingComm Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.movingcommtech.com