How do the four nodes of Bluetooth Mesh work?
Bluetooth Mesh technology has gained significant attention among engineers due to its open standards, low cost, and high performance. It addresses the limitations of low-power Bluetooth, which previously struggled with network connectivity in real-world applications. By supporting mesh networking, Bluetooth Mesh enables more robust and scalable communication between devices, making it an ideal choice for building automation and other smart systems.
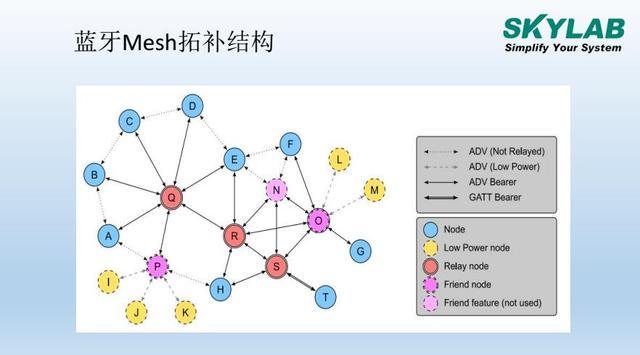
With Bluetooth Mesh, you can build large-scale networks that allow secure and reliable communication across thousands of devices. The network is structured around key components such as Nodes, Elements, Models, and States. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the nodes in a Bluetooth Mesh network, explaining how they become active members of the network.
The Bluetooth Mesh specification outlines four types of nodes: Relay Node, Low-Power Node (LPN), Friend Node, and Proxy Node.
- **Relay Node**: This node receives and retransmits mesh messages via the broadcast bearer layer, helping to expand the network’s coverage.
- **Proxy Node**: It acts as a bridge between the GATT interface and the broadcast bearer layer, allowing non-mesh-enabled devices to interact with the network.
- **Low-Power Node (LPN)**: Designed for energy efficiency, LPNs operate with minimal receiver activity, waking up only when necessary. They maintain a connection with a Friend Node to receive messages when needed.
- **Friend Node**: This node stores messages intended for LPNs and forwards them when the LPN is ready to receive, ensuring efficient communication without constant power drain.
Relay nodes play a crucial role in propagating data throughout the network, but their continuous operation increases power consumption. While Bluetooth Low Energy is already more power-efficient than many alternatives, some applications—like smart lighting—can still rely on a constant power source. However, for battery-powered or energy-harvesting devices, this approach isn’t always feasible.
To address this, the concept of a Low-Power Node was introduced. These nodes work in tandem with a "buddy" or Friend Node, which remains active and caches messages. The LPN then wakes up periodically to receive and process information before returning to sleep mode, significantly extending battery life.
Proxy Nodes are also essential, as they enable devices like smartphones—which support Bluetooth Low Energy but not Bluetooth Mesh—to connect to the mesh network. Communication happens through the GATT interface, making it easier for everyday devices to participate in smart environments.
**Bluetooth Mesh Networking Solution**
Bluetooth Mesh is a powerful new topology for Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) that supports many-to-many device communication. It allows the creation of extensive networks with dozens, hundreds, or even thousands of devices, enabling seamless interaction and data exchange. This makes it a perfect fit for applications like building automation, wireless sensor networks, and asset tracking.

The Bluetooth Mesh networking solution is exemplified by BLE modules like the SKB369. With Bluetooth Mesh, all functions in a smart home system can be controlled effortlessly from a single device. Its scalable architecture is not limited to homes; it can be expanded to meet the needs of offices, factories, industrial settings, and even entire cities, connecting millions of nodes reliably and efficiently.
Co-extruded (double Wall) Heat Shrinkable Tubing
Co-extruded (double wall) heat shrinkable tubing
Co-extruded (double wall) heat shrinkable tubing,Heat-shrink tube,Heat shrinkable tubing,thermal contraction pipe,Shrink tube
Mianyang Dongyao New Material Co. , https://www.mydyxc.com