"Graphene battery" is just a pseudo-concept, ordinary battery + 1% graphene germanium graphene battery
Let's first look at what exactly is graphene. In 2004, Andrea of ​​the University of Manchester, UK? Gam and Constantine? Novo Shalov stripped the graphene from the graphite flakes, and the two won the 2010 Nobel Prize in Physics. The graphene here is a honeycomb lattice two-dimensional atomic crystal composed of a single layer of carbon atoms, and has a theoretical thickness of only 0.34 nm. It has excellent electrical properties such as electrical conductivity, heat conduction and barrier properties, and thus it is in the field of batteries. The application is favored by many people and is called the "king of materials."

For example, in order to obtain graphene samples with the best electrical and mechanical properties, it still needs to rely on the most time-consuming and cost-effective means - mechanical stripping method, that is, tape is adhered to graphite, and graphene is manually isolated. In 2004, Novoselov, they produced graphene in this way. Although the required equipment and technical content seem to be low, the problem is that the success rate is lower. It is OK to get some samples for research. If it is industrialized, such a means is useless, that is, master the graphite of the world. The mine also has no commercial value.
Gao Hongjun, a member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and a researcher at the Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, said that in practical applications, only graphene without any defects has strong properties. Otherwise, the strength of the entire graphene product is greatly reduced. In fact, it is such an obstacle, it is too early to realize the large-scale commercial production of graphene batteries in the true sense.
Liu Guanwei, a senior engineer at the Beijing Research Institute of Nonferrous Metals and a Ph.D. student at Tsinghua University, said in an interview with Beijing Science and Technology News that even if some companies claim to have new graphene products, graphene is often used as an additive in this product. Role, which is no exception in the battery field.
Professor Huang Xuejie, head of the Solid State Ionology Research Group at the Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, believes that adding a small amount of graphene to the positive electrode can increase the electronic conductance of the positive electrode and improve the discharge rate characteristics of the battery, but generally it is less than one percent. It is said that a lithium ion battery with a little graphene has become a graphene battery.
What's more, the current graphene battery is only added with some graphite sheet components called multilayer graphene. In theory, single-layer graphene has the best conductivity, and is used for short battery charging time, and the more layers, the worse the conductivity, and the longer the battery charging time. At present, few companies dare to claim that they use a single layer of graphene to make a battery, and more use only a mixture of graphene, specifically a small multilayer graphite microchip containing a small amount of graphene.
It is the rigorous research institutions that do not dare to use graphene batteries when publishing authoritative papers. In mid-December 2015, the research team of the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences issued a report in Science, which pointed out that it developed a high-performance supercapacitor electrode material, and some media praised: "The material has excellent electrochemical energy storage. Features, can be used as an electric vehicle's 'super battery', the biggest highlight of this battery is charging for 7 minutes, driving 35 kilometers." Then the graphene battery concept was smashed. However, the official website of Shanghai Silicate Institute gave the news: "The research team led by Huang Fuqiang, a researcher at the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, collaborated with researchers from Peking University and the University of Pennsylvania to synthesize an orderly Holes (the meaning of mesopores) are new materials with less carbon." And the paper in the journal Science does not mention graphene, but carbon.
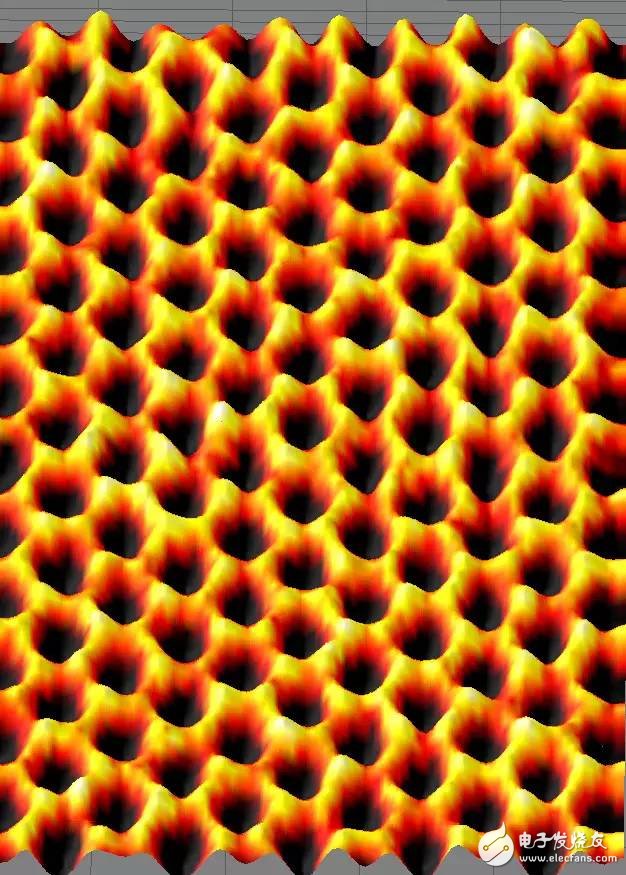
Graphene monolayer carbon atom structure observed by electron microscope
In the academic world, the current graphene battery is still a pseudo-concept, and the current graphene battery does not exist. There are dozens of listed companies in China that have laid out graphene power batteries. However, there are few products that can be mass-produced. And there is no graphene battery that can be produced on a large scale in the world.
Nowadays, many companies are speculating about this concept, and its gimmick is far more meaningful than practical value. The high specific surface area and other properties of the nanomaterials of the graphene material itself are not compatible with the current technical system of the lithium ion battery industry, so the hope of application is very slim. Therefore, the current application of graphene on the battery is mainly combined with silicon in the negative electrode of the battery to replace the original graphite, so that it can absorb more charge, improve the conductivity of the battery, reduce the resistance of charge and discharge, and the performance improvement effect is only This is the limit. In fact, in the field of new energy batteries, the so-called disruptive theory of graphene batteries has never been recognized by the industry. Although graphene can be used as a conductive agent to promote rapid charge and discharge of lithium batteries, theoretically, it can improve the rate performance. However, if the dispersion process is not in place and the mixing is uneven, it is still difficult to exert its effect.
According to the current development trend, graphene may be promising in terms of new flexible batteries, devices, displays, and catalysts. But in terms of batteries, it is not optimistic.
Graphene is too expensive, even if it is made into a battery, ordinary consumers can't bear it.In the application of lithium batteries, graphene mainly plays a role, one is the conductive agent, and the other is the electrode lithium intercalation material. In fact, both of these are in competition with traditional conductive carbon/graphite. "The question is coming. Do you know that conductive carbon/graphite is cheaper? It’s all about tons of tons. Can you sell the graphene that can be reduced to this price? Now all kinds of materials used in lithium batteries are one ton. Tens of thousands, about 100,000 things, and every day bear the pressure to reduce prices, the use of graphene is completely unrealistic." This is mainly because graphene is too expensive. One gram of thousands of prices, this is not something that ordinary companies can afford. A few years ago, the price of graphene was as high as 5,000 yuan per gram, far exceeding the price of gold. In addition, it is such a battery that is made out and consumers are unbearable.
Recently, some market analysts claimed that the complete industrial chain of graphene products and high-efficiency battery projects in China has been formed. In fact, China's current graphene materials are in a critical period from laboratory to industrialization, and the maturity of production technology is not high. Due to factors such as the long application path of industrialization, the mass production of graphene has not been fully realized. Some people think that this process has not been realized, it is completely idiotic to say that our graphene battery can achieve large-scale industrial production.
Therefore, some sober and industry insiders believe that it is too early to say that China has produced a graphene battery.
IP 20 frequency inverter for three-phase asynchronous motors, specially designed for pump and fan applications in the following market segments: Water & Wastewater, Oil & Gas, building management and energy plant.
Three Phases Inverter Elrctric,Period To Frequency Converter,Three Phases Frequency Converter,Wavelength To Frequency Inverter
Wuxi Trenty Machinery & Equipment Co., Ltd. , https://www.elec-inverter.com
