How to correctly connect the batteries in series and in parallel
How to properly connect the batteries in series and in parallel, it sounds simple, but with some simple rules, you can avoid unnecessary problems.
In the battery pack, a plurality of batteries are connected in series to obtain a required operating voltage. If you need higher capacity and more current, you should connect the batteries in parallel. There are also some battery packs that combine the two methods of series and parallel. The battery of a laptop computer may be connected in series with four 3.6V lithium-ion batteries, the total voltage reaches 14.4V; then, the two groups of batteries connected in series are connected in parallel, so that the total power of the battery pack can be Increased from 2000 mAh to 4000 mAh. This connection is called "four-string two-in-one", which means that two sets of battery packs connected in series by four batteries are connected in parallel.
A battery is generally used in watches, backup memories, and cellular phones. The nominal voltage of a nickel-based battery is 1.2V, the alkaline battery is 1.5V, the silver oxide battery is 1.6V, the lead acid battery is 2V, the lithium battery is 3V, and the lithium-ion battery has a nominal voltage of 3.6. V. Using lithium ion polymers and other types of lithium batteries, it is rated at 3.7V. If you want to get an unusual voltage like 11.1V, you have to connect three batteries in series. With the development of modern microelectronics technology, we have been able to power a cellular phone and low-power portable communication products with a 3.6V lithium-ion battery. In the 1960s, mercury batteries, which were widely used in illuminance meters, have now completely withdrawn from the market due to environmental concerns.
Nickel-based batteries have a nominal voltage of 1.2V or 1.25V. There is no difference between them except for market preferences. Most commercial batteries have a voltage of 1.2V per cell. For industrial, aerospace and military batteries, the voltage of each cell is still 1.25V.
Tandem
Portable devices that require high power are typically powered by a battery pack in which two or more cells are connected in series. If a high voltage battery is used, the size of the conductors and switches can be made small. Mid-priced industrial power tools typically use batteries powered from 12V to 19.2V, while advanced power tools use batteries from 24V to 36V for greater power. The automotive industry eventually increased the ignition cell voltage of the starter from 12V (actually 14V) to 36V, or even 42V. These battery packs are made up of 18 lead-acid batteries in series. In the early hybrid cars, the battery pack used to supply power had a voltage of 148V. The battery packs used in the newer models have voltages ranging from 450V to 500V, mostly nickel-based chemical batteries. A nickel-metal hydride battery pack with a voltage of 480V is made up of 400 nickel-metal hydride batteries in series. Some hybrid cars have also been tested with lead acid batteries.
The 42 V car battery is expensive, and it produces more arc on the switch than the 12V battery. Another problem with using a high-voltage battery pack is that it is possible to experience a failure of a certain battery in the battery pack. It's like a chain, the more batteries are connected in series, the higher the chance of this happening. As long as there is a problem with one of the batteries, its voltage will decrease. At the end of the day, a “disconnected†battery may interrupt the delivery of current. It is not easy to replace the "bad" battery, because the old and new batteries do not match each other. In general, the capacity of new batteries is much higher than that of older batteries.
Let's look at an example of a battery pack. The third battery produces only 0.6V instead of the normal 1.2V (Figure 1). As the operating voltage drops, it reaches the critical point of discharge end faster than the normal battery pack, and its use time is also drastically shortened. Once the device is powered off due to low voltage, the remaining three good batteries will not be able to send the stored power. At this time, the third battery also exhibits a large internal resistance. If the load is also present at this time, the output voltage of the entire battery chain will be greatly reduced. In a set of serial batteries, a poorly performing battery, like a plug that blocks a water pipe, creates a huge amount of resistance that prevents current from flowing. The third cell will also be shorted, which will reduce the terminal voltage to 3.6V, or disconnect the battery pack link and cut off the current. The performance of a battery pack depends on the performance of the worst battery in the battery pack.

in parallel
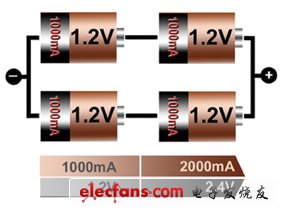
In order to get more power, you can connect two or more batteries in parallel. In addition to paralleling the batteries, another option is to use a larger battery. This approach does not apply to all situations due to the limitations of the battery that can be used. In addition, large-sized batteries are not suitable for the form factor required for a dedicated battery. Most chemical batteries can be used in parallel, while lithium-ion batteries are best suited for parallel use. The battery pack consisting of four cells in parallel maintains a voltage of 1.2V while the current and run time are increased by a factor of four.
Examples of battery packs have a lower impact on high-impedance or "open-circuit" batteries in battery parallel circuits compared to battery series, but parallel battery packs reduce load capacity and reduce run time. This is like an engine that only starts three cylinders. The damage caused by a short circuit is greater because, in the event of a short circuit, the failed battery quickly drains the battery and causes a fire (Figure 2).

Series and parallel
When using a series-parallel connection method, it is flexible in design and can achieve the required voltage and current with a standard battery size (Figure 3). It should be noted that the total power will not change due to the different connection methods of the battery. The power is equal to the voltage multiplied by the current.
For lithium-ion batteries, series-parallel connection methods are common. One of the most commonly used battery packs is the 18650 (18 mm diameter and 650 mm length). It has a protection circuit that monitors each cell in series, so its maximum actual voltage is 14.4 V. This protection circuit can also be used to monitor the status of each cell in parallel.
Household battery
The connection methods of the series and parallel connection of the batteries mentioned above are directed to rechargeable battery packs in which the batteries are permanently welded together. The rules described above apply to household batteries, except that several batteries are placed in the battery compartment where the battery is installed, in series. When connecting several batteries in series, the following basic requirements must be observed:
â— Keep the connection points of the battery clean. When four batteries are used in series, there are eight connection points (the connection point from the battery to the battery room, and the connection point from the battery room to the next battery). There is a certain resistance at each connection point. If the connection point is increased, it may affect the performance of the entire battery pack.
â— Do not mix batteries. When the battery is low, replace all batteries. When used in series, use the same type of battery.
â— Do not charge the non-rechargeable battery. When charging a non-rechargeable battery, hydrogen is generated, which may cause an explosion.
â— Pay attention to the polarity of the battery. If the polarity of one of the batteries is reversed, the voltage of the entire string will be reduced instead of increasing the voltage.
â— Take the fully discharged battery out of the suspended device. Older batteries are more prone to leakage and corrosion. Alkaline batteries are less problematic than carbon zinc batteries.
â— Do not put the batteries in a box, as this may cause a short circuit. A short circuit in the battery can cause heat and cause a fire. Please put the discarded battery in a small plastic bag and insulate it from the outside.
â— A primary battery pack similar to an alkaline battery can be thrown into a regular trash can. However, it is best to send the used battery to the regeneration cycle.
LED wall washers are high
power LED lights that are used for decorative lighting and highlight, or wash
walls, of buildings, clubs, hotels, stages, parks, plazas, commercial building
facades, art galleries, etc., with different kind of colors.
The LED wall washer can even change their colors while projecting. The RGB LED
wall washer lights can project various colors and change the color by
programming the LED wall washer the way you want to. LED wall washers can be
used for clubs, stages, parks, plazas, commercial building, art gallery,
landscape, architectural decoration, etc.
Indoor Wall Washer,Led Christmas Wall Washer,Led Light Wall Washer,Led Outdoor Wall Washer
ZHONGSHAN G-LIGHTS LIGHTING CO., LTD. , https://www.glightsled.com
